上了一下午班(课),经典赛后解题.
不然就二血了(逃
题目代码:https://paste.ubuntu.com/p/MPWw3SGMcz/
首先验一下N1和N2,发现两个都不是素数,于是yafu分解一下,N2可以很快分解出来,然后发现有一个因子跟N1是相同的,于是得到:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| p1 = 297342668339361548416629796745639177971
q1 = 92636417177965240871815246762704348071
assert p1*q1 == N1
p2 = 69857405335111415530599248077
q2 = 92636417177965240871815246762704348071
assert p2*q2 == N2
|
根据[Jous21]里的Theorem 4.4,如果n=n1∗n2的话,就会有EA,B(Zn)同构于EA,B(Zn1)⨁EA,B(Zn2),而且如果点P在EA,B(Zn)的话,点P1≡P (mod n1)和点P2≡P (mod n2)也会分别在EA,B(Zn1)和EA,B(Zn2)中:

所以给定Q=xP in EA,B(Zn)的话,可以先分别求出x1=QP−1 in EA,B(Zn1)和x2=QP−1 in EA,B(Zn2),然后用x1和x2做个CRT就可以得到x了(但要注意模数是用EA,B(Zni)的阶,不是Zni的阶);也就是可以解出题中的d1和d2,然后解出flag;
经实验,q1和q2是相对容易解的,因为EA,B(Zq1)和EA,B(Zq2)的群阶可以分解成若干小的素数,用Pohlig–Hellman algorithm可以很快解出;p2分解出来的素数会大一点,但也算是可解的;Sage中的discrete_log好像就是直接用Pohlig–Hellman的,在椭圆曲线上的用法可以参考一下这个gist;
对于p1的话,EA,B(Zp1)的群阶是个大素数,但是和p1是相等的,可以用Smart’s attack解,exp里copy了stackexchange里的一个回答的代码;于是最终脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
import libnum
def SmartAttack(P,Q,p):
E = P.curve()
Eqp = EllipticCurve(Qp(p, 2), [ ZZ(t) + randint(0,p)*p for t in E.a_invariants() ])
P_Qps = Eqp.lift_x(ZZ(P.xy()[0]), all=True)
for P_Qp in P_Qps:
if GF(p)(P_Qp.xy()[1]) == P.xy()[1]:
break
Q_Qps = Eqp.lift_x(ZZ(Q.xy()[0]), all=True)
for Q_Qp in Q_Qps:
if GF(p)(Q_Qp.xy()[1]) == Q.xy()[1]:
break
p_times_P = p*P_Qp
p_times_Q = p*Q_Qp
x_P,y_P = p_times_P.xy()
x_Q,y_Q = p_times_Q.xy()
phi_P = -(x_P/y_P)
phi_Q = -(x_Q/y_Q)
k = phi_Q/phi_P
return ZZ(k)
N1 = 27544759469094453505371358768052861416297003882211878831861112512567899543941
A1 = 4208715803791813173086894172778966025419787767340027559010619240548499823390
B1 = 11846440123913040489420209031751160809904311707943252241515965930654415480691
P1x = 479750084250968709343887919962436485997147832319843477221083468203689368148
P1y = 15452861783577624143044213767588871736433639621547613407582902947429567101675
p1 = 297342668339361548416629796745639177971
q1 = 92636417177965240871815246762704348071
assert p1*q1 == N1
Gp1 = GF(p1)
Ep1 = EllipticCurve(Gp1, [0, 0, 0, A1, B1])
gp1 = Ep1([P1x, P1y])
yp1 = Ep1([
14736970297054248276364510675718632926198693034158620007675880103924809577805,
3447209262654420855289144268810543114387612255490962015335062266658385100211
])
xp1 = SmartAttack(gp1, yp1, p1)
print('xp1 = %d' % xp1)
Gq1 = GF(q1)
Eq1 = EllipticCurve(Gq1, [0, 0, 0, A1, B1])
gq1 = Eq1([P1x, P1y])
yq1 = Eq1([
14736970297054248276364510675718632926198693034158620007675880103924809577805,
3447209262654420855289144268810543114387612255490962015335062266658385100211
])
xq1 = discrete_log(yq1, gq1, gq1.order(), operation='+')
print('xq1 = %d' % xq1)
op1 = gp1.order()
oq1 = gq1.order()
x1 = crt([xp1, xq1], [op1, oq1])
flag1 = libnum.n2s(int(x1))
print(flag1)
N2 = 6471339743593595797696002766822660599108196938080465998531085409467
A2 = 3199218821393204771660095172457569312269694438403110131957204042314
B2 = 762889472027318213897694878260359911054972690369935049954326689904
P2x = 2557373437970770011124755960432555084678930336188254243278984381842
P2y = 4442763096366920105760404533052204677305995021662082361185473321644
p2 = 69857405335111415530599248077
q2 = 92636417177965240871815246762704348071
assert p2*q2 == N2
Gp2 = GF(p2)
Ep2 = EllipticCurve(Gp2, [0, 0, 0, A2, B2])
gp2 = Ep2([P2x, P2y])
yp2 = Ep2([
4834036103940457959470026215023033401071737087504569417466448644066,
5511016821581393405975510064568222454318072088628361854656950557373
])
xp2 = discrete_log(yp2, gp2, gp2.order(), operation='+')
print('xp2 = %d' % xp2)
Gq2 = GF(q2)
Eq2 = EllipticCurve(Gq2, [0, 0, 0, A2, B2])
gq2 = Eq2([P2x, P2y])
yq2 = Eq2([
4834036103940457959470026215023033401071737087504569417466448644066,
5511016821581393405975510064568222454318072088628361854656950557373
])
xq2 = discrete_log(yq2, gq2, gq2.order(), operation='+')
print('xq2 = %d' % xq2)
op2 = gp2.order()
oq2 = gq2.order()
x2 = crt([xp2, xq2], [op2, oq2])
flag2 = libnum.n2s(int(x2))
print(flag2)
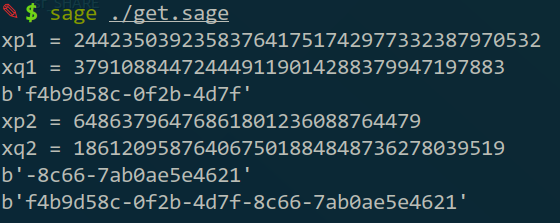
flag = flag1+flag2
print(flag)
|
[Jous21] Jousma W. Elliptic curves: an Introduction and Their Group Structure Over Z/NZ[D]. , 2021.
[Smart99] Smart N P. The discrete logarithm problem on elliptic curves of trace one[J]. Journal of cryptology, 1999, 12(3): 193-196.
[Muss06] Musson M. Attacking the Elliptec Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem[M]. Acadia University, 2006.
